Ultrasonic Assembly Process
Ultrasonic Assembly Process
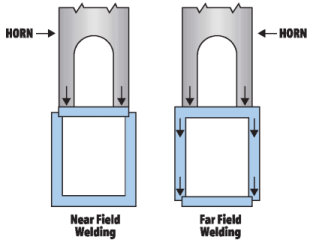
In Ultrasonic welding, high frequency sound energy is used to bring the joining surfaces of two thermoplastic parts to a molten state where they can be permanently welded together.
- The horn, under pressure from the assembly stand, contacts one of the two mated plastic parts.
- Vibrational energy from the horn causes the contacted plastic part to vibrate against its mate.
- The mechanical vibration of one part against the second causes frictional heat, which melts the plastic parts at their interface and allows the two surfaces to molecularly fuse together.
- After a short cooling time, a permanent, homogeneous weld results.