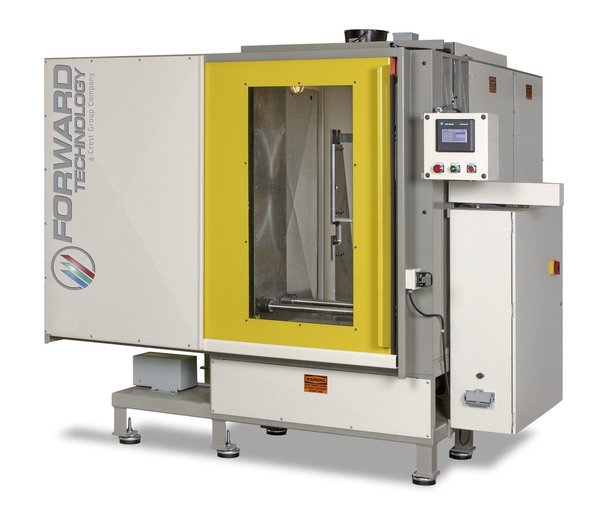
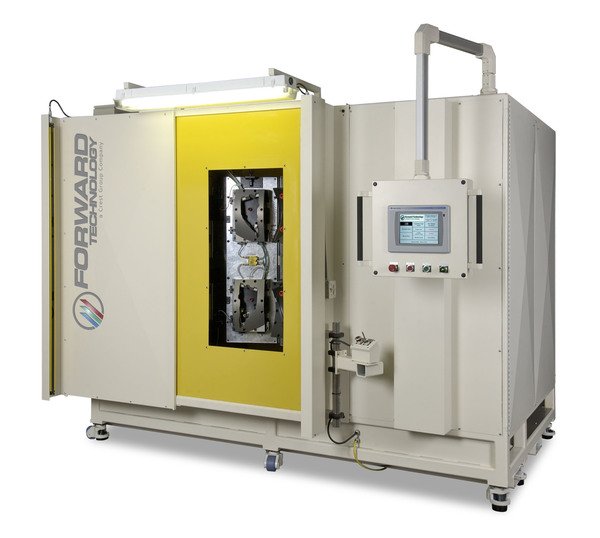
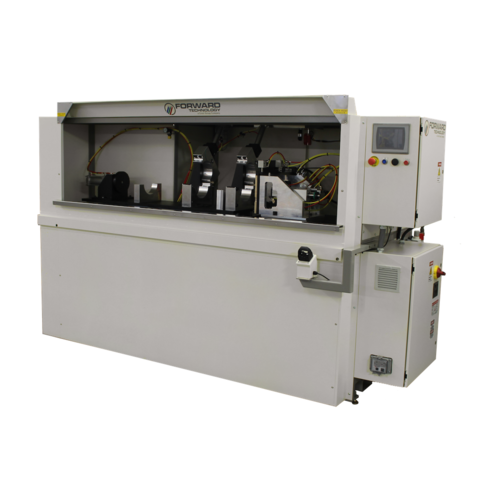
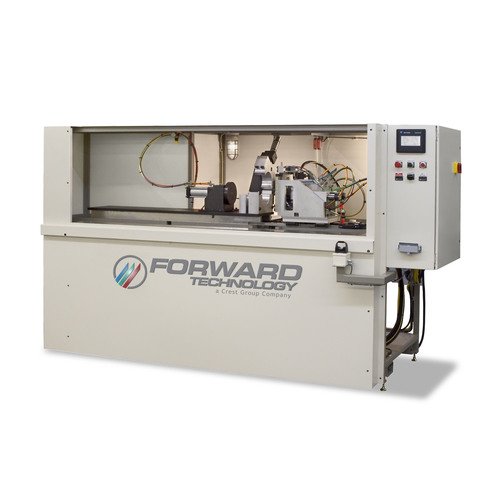
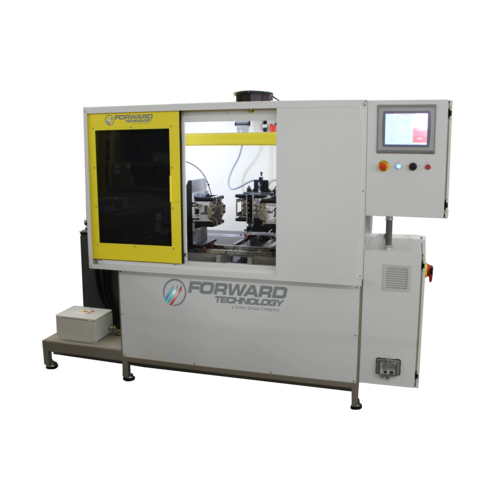
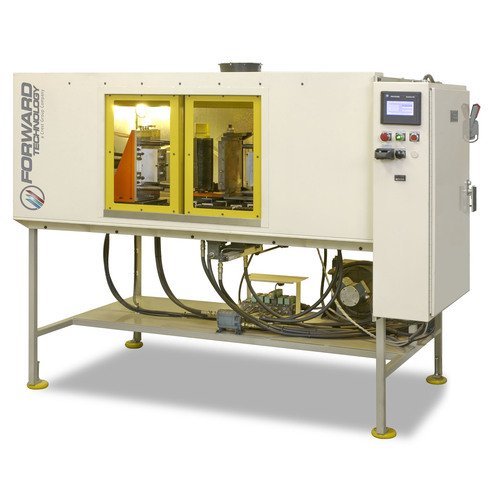
Infrared Welders
Infrared welding is a welding technique used for challenging materials and large part assembly with high strength and hermetic requirements.
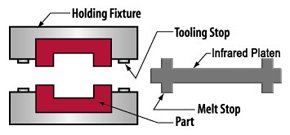
During Infrared welding, both part halves are held rigidly in position near an infrared emitting platen to melt the joining surfaces. The platen is removed and the part halves driven together and allowed to re-solidify under pressure.
Forward has manufactured infrared systems since 2004 and hot plate welders (the platform for infrared welding) since 1965. Our experience has resulted in the design of equipment based on ultra-rigid construction and detailed melt control to ensure precise repeatability of part quality, year after year of production.
Vertical or horizontal platen configurations are available. From manually loaded and unloaded machines to semi and fully automated in-line systems, Forward offers the widest array of standard products designed to accommodate most product sizes.
Forward also offers standard quartz IR emitter arrays in addition to metal foil IR. Metal foil IR allows for complex geometry and a reduced array cost.
About Infrared Welding
Welding Non-contact thermal welding technique
Infrared Process Advantages
Fast, flexible and accurate
Designing for Infrared Welding
Weld materials and joint designs
Infrared Weld Tooling
Standards, advantages and options
Infrared vs. Other Welding Methods
Comparison of welding techniques
Download our Infrared Welder Brochure
We're Here to Help
Have A Question About A Product Or Service?
About Infrared Welding
Infrared welding is a non-contact thermal welding technique capable of producing very strong, air-tight welds in thermoplastic parts.
When using this energy in a tightly controlled manner, thermoplastic parts can be heated to molten temperatures very quickly and then joined together in a manner very closely resembling hot plate welding.
Based on the properties of the plastic to be welded:
- Most of the infrared radiation is absorbed within the material.
- Some of the infrared radiation is reflected off of the surface of the material
- Some of the infrared radiation penetrates through the material.
Infrared Welding Joint Designs
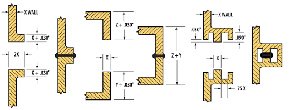
As with the hot plate welding process, infrared welding produces a welded joint which often yields a weld strength that is equal to or stronger than any other area of the part.
Material displacement is typically 0.030" total. This results only from 0.015" material displacement per side from material fusion during the weld/seal step as there is no displacement during the infrared melt step.
This may vary depending on part material and geometry. We strongly recommend discussing your joint design with one of our application engineers before arriving at your final part design.
Infrared weld joint designs include flanged butt joint, straight butt joint, butt joint with flash trap, recessed joint with flash trap.
Infrared vs. Other Welding Methods
We break down how Infrared Welding compares versus the other welding methods of Vibration and Hot Plate.
Our welding method comparison looks at:
- Accuracy
- Temperature Control
- Pre-heating & cool down
- Power requirements
- Cost estimates
- Insert or coating materials
- Design flexibility
- More







